
Basic Sleep & Sleep Hygiene Education
Sleep education and sleep hygiene information includes general recommendations and information relating to environmental factors, physiologic factors, behaviour and habits that that aim to improve and maintain good sleep.
Sleep hygiene information alone is not a sufficient treatment for insomnia. It should be paired with evidence-based behavioural treatment such as BBTi, or CBTi, including bedtime restriction therapy and/or stimulus control therapy.
Basic sleep information
It is important to provide the patient with basic information about the structure of sleep during the night, and some of the factors that control our sleep (Process S, Process C).
Sleep consists of a repetition of 4 to 6 sleep cycles on average throughout the night with the first cycles of the night being shorter than the later cycles.
A sleep cycle consist of 4 sleep stages and lasts about 90 minutes:
- Stage 1: Lightest stage of sleep, still have drifting thoughts, easiest to wake up
- Stage 2: Moderate stage of sleep, unique brain wave activity, slightly harder to wake up
- Stage 3: Deepest stage of sleep, hardest to wake up
- REM Sleep: Associated with rapid eye movements and vivid dreams

Source: Alexander Sweetman
Older age reduces time of the REM stage.
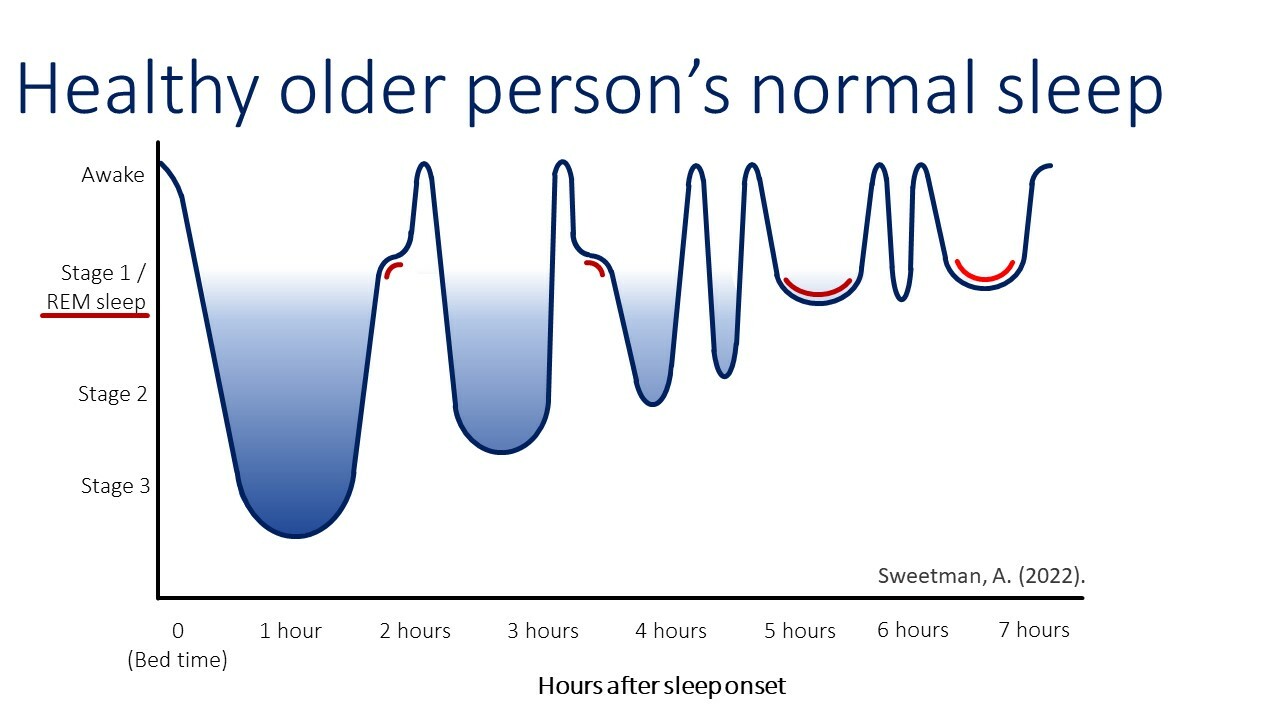
Source: Alexander Sweetman
The deep sleep and REM sleep stages are of particular importance to the recuperation of body and brain. Circadian rhythm (our body clock) regulates the sleep-wake cycle. The sleep-wake cycle is described to be regulated by the interplay of Process S, which promotes sleep, and Process C, which maintains the biological clock and controls the timing of our sleep and wake patterns. Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation: An Unmet Public Health Problem. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Sleep Medicine and Research; Colten HR, Altevogt BM, editors. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US) 2006
The need for sleep (Process S) accumulates across the day, peaks just before bedtime at night and dissipates throughout the night. Attempting to sleep when not having acquired sufficient sleep pressure (Process S) will make it more difficult to fall asleep, or may lead to (longer) nocturnal awakenings. 1

Source: Alexander Sweetman
Basic sleep information can help the patient understand the rationale for Bedtime Restriction Therapy, and promote sustained engagement with this treatment. The restricted sleep period on one night will result in greater sleep pressure towards the evening, which will promote to fall asleep easier with shorter wake-time during the subsequent night. 1

Source: Alexander Sweetman
|
General Sleep Health Information for patients is available on the Sleep Health Foundation website.
AHI - Apnoea-Hypopnoea Index
BBTi - Brief Behavioural Therapy for Insomnia
BMI - Body Mass Index (kg/m2)
BQ - Berlin Questionnaire
CBTi - Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Insomnia
CELL - Coblation Endoscopic Lingual Lightening
COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
CVA - Cerebrovascular Accident
CPAP - Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
CSA - Central Sleep Apnoea
DASS - Depression Anxiety Stress Scale
DBAS - Dysfunctional Beliefs and Attitudes about Sleep
DBP - Diastolic Blood Pressure
DIMS - Difficulties Initiating and/or Maintaining Sleep
DISE - Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy
DISS - Daytime Insomnia Symptom Scale
ENT - Ear Nose and Throat
ESS - Epworth Sleepiness Scale
FOSQ - Functional Outcomes of Sleep Questionnaire
FSH - Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
FTP - Friedman Tong Position
GP - General Practitioner
HANDI - RACGP Handbook of Non-Drug Interventions
HGNS - Hypoglossal Herve Htimulation
ISI - Insomnia Severity Index
K10 - Kessler Psychological Distress Scale
MAD - Mandibular Advancement Device
MAS - Mandibular Advancement Rplint
MBS - Medicare Benefits Schedule
MMA - Maxillomandibular Advancement Surgery
MRA - Mandibular Repositioning Appliance
ODI - Oxygenation Desaturation Index
OSA - Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
PLMD - Periodic Limb Movement Disorder
PT - Positional Therapy
PTSD - Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
PSG - Polysomnography
QSQ - Quebec Sleep Questionnaire
REM - Rapid Eye Movement
RFTB - Radiofrequency Thermotherapy of the Tongue Base
SBP - Systolic Blood Pressure
SCI - Sleep Condition Indicator
SE - Sleep Efficiency
SF36 - Short-Form (36) Health Survey
SMILE - Submucosal Minimally Invasive Lingual Excision
SNRIs - Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
SOL - Sleep Onset Latency
SSRI - Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
TFTs - Thyroid Function Tests
TIB - Time In Bed
TORS - Transoral Robotic Surgery
TST - Total Sleep Time
UPPP - Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
WASO - Wake After Sleep Onset